How You Can Use 3D Printing and Scanning to Create Prototypes
In the dynamic design and development world, 3D printing and scanning are pillars of innovation, offering unparalleled flexibility and precision in prototyping. These technologies reshape how ideas are brought from concept to reality across various industries.
Here is some information on the practical use of 3D printing and scanning in creating prototypes, ensuring your projects are visionary and tangible.
Role of 3D Scanning in Prototyping
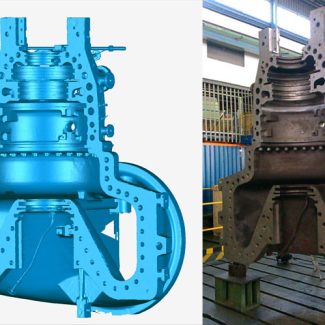
When it comes to 3D scanning, it’s true that it serves as the bridge between the physical world and digital design. It captures the intricate details of an object, translating them into a digital format. This process is crucial for replicating or integrating existing objects into new designs.
Here are some beginning steps to use 3D scanning for prototype production:
- Capturing the Details. Use a 3D scanner to digitize the object you wish to prototype. This step is vital for ensuring accuracy in dimensions and details.
- Digital Refinement. Import the scan into CAD (computer-aided design) software. Here, you can tweak or merge it with new designs, preparing it for 3D printing.
3D Printing and Prototype Creation
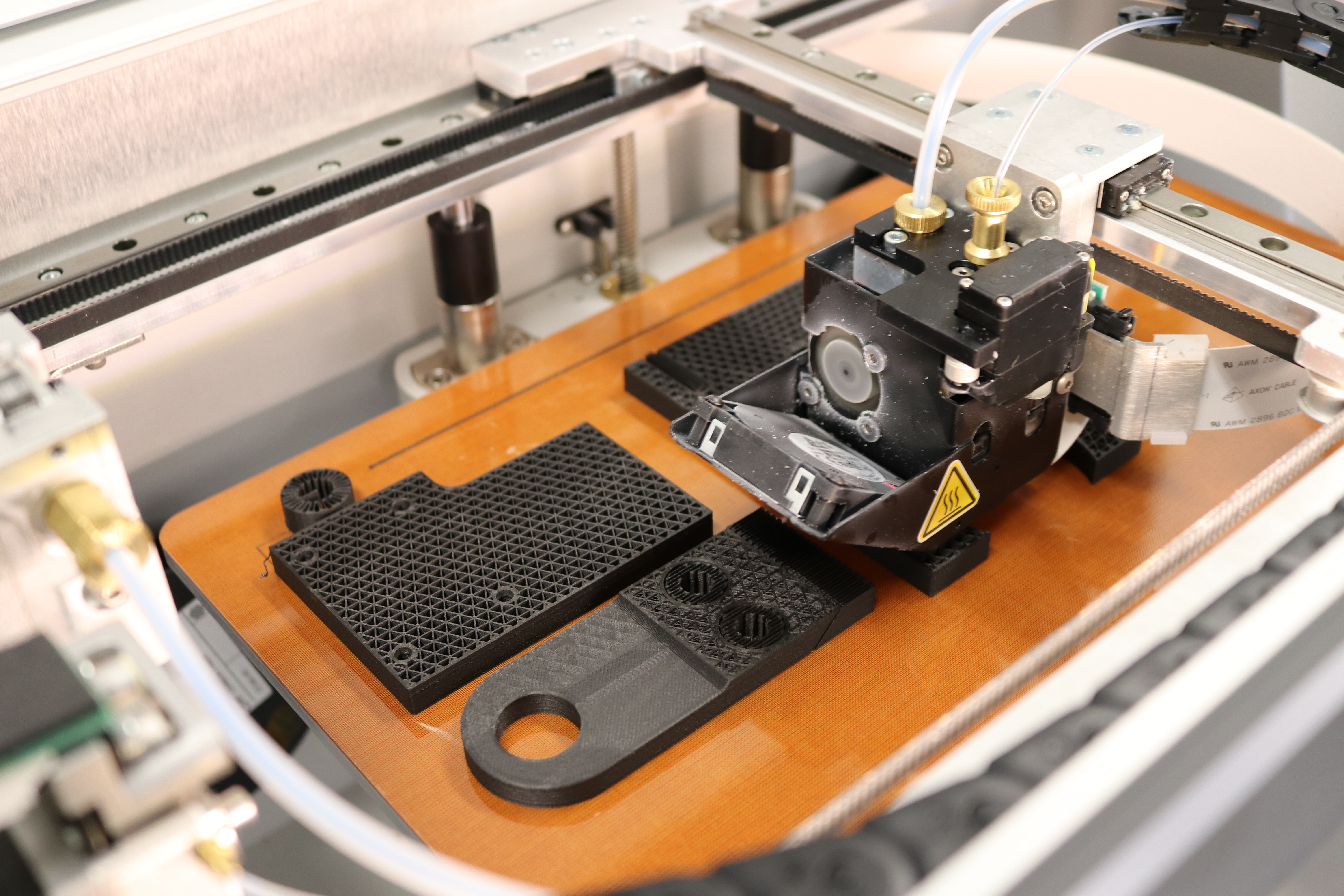
3D printing transforms digital models into physical prototypes. It allows for experimenting with complex designs that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. Here are some basic steps to use 3D printing for prototype creation:
- Material Selection. Choose a material that aligns with your prototype’s purpose – be it plastic for flexibility or metal for durability. The most common ones are PLA and Graphene.
- Printing Process. The 3D printer will layer your chosen material, meticulously building your design from the ground up.
- Post-Processing. After printing, you may need to refine the prototype through sanding, painting, or assembly.
Iterative Design: Test, Tweak, Repeat
The beauty of 3D printing and scanning lies in their facilitation of rapid prototyping. This iterative process involves multiple steps that are listed below:
- Testing. Evaluate the prototype’s form and function. In this step, you must analyze if the end product meets the intended design criteria.
- Revising. Based on feedback, adjust the digital model. This step is crucial for refining the prototype.
- Reprinting. Print the revised design. Repeat this cycle until the prototype meets all your specifications.
Applications Across Industries
The applications and uses of 3D printing are vast and expanding with every passing second. From healthcare, where custom prosthetics are printed, to aerospace, where parts are prototyped for efficiency, 3D printing and scanning are versatile tools. These technologies are also used in architecture for model building and in education for interactive learning tools.
Evolution of Prototyping
The future of this tech lies in its ability to handle multiple materials. It also includes advanced composites and metals. This versatility will open new avenues for prototype development. Plus, it will allow for more complex and functional designs.
As 3D printing and scanning become more advanced and affordable, their applications are expected to expand beyond traditional prototyping—the vast and varied possibilities, from customized medical implants to intricate architectural models. We are moving towards a future where multi-material printing is commonplace, opening even more opportunities in prototype development.
3D printing and scanning are more than just technological advancements; they are the keystones of modern prototyping. By comprehending and utilizing these tools, you can transform your abstract ideas into tangible, testable prototypes, pushing the boundaries of innovation and creativity.