Using 3D Scanning for Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering deconstructs an existing product or component to understand its functionality. It is crucial in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. One of the essential tools that has revolutionized the reverse engineering process is 3D scanning. Below is the use of 3D scanning for reverse engineering and its benefits.
Basics of 3D Scanning
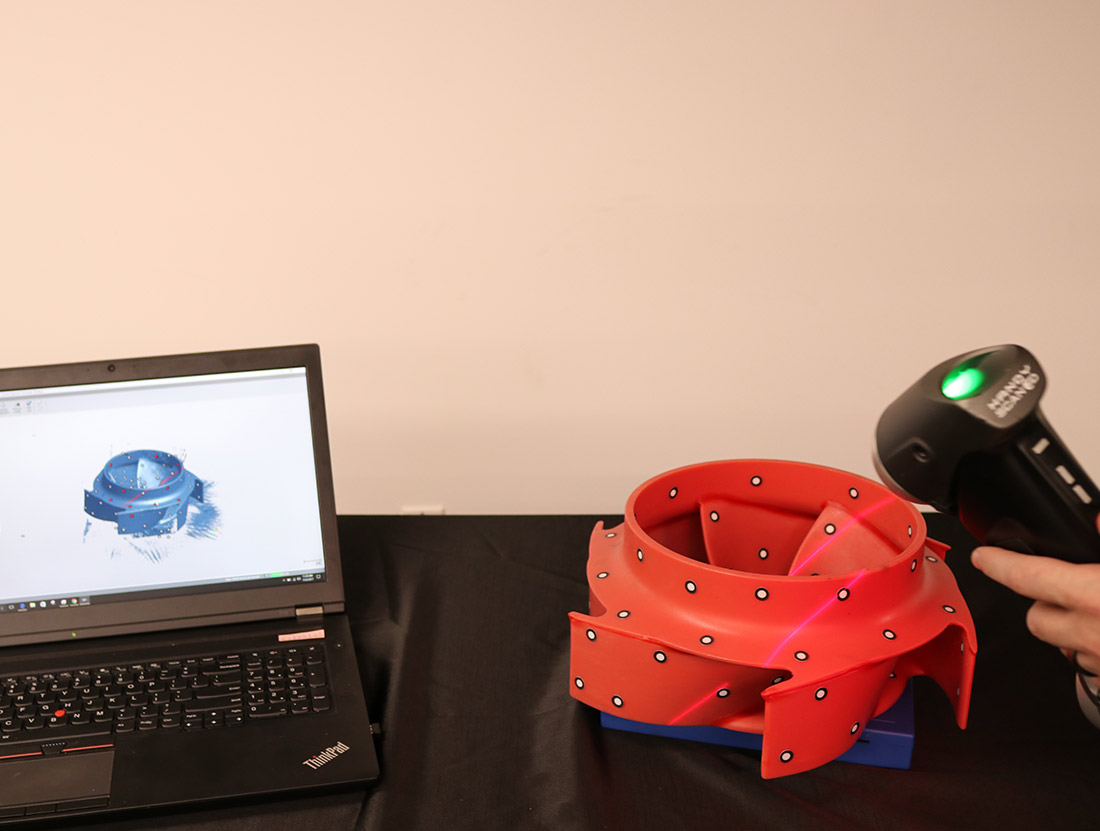
Before delving into its application for reverse engineering, you need to understand the basics of 3D scanning. 3D scanning is a non-contact technology that uses various methods to capture the surface geometry of an object. These scanners create a point cloud, a dense collection of 3D data points representing the object’s surface. This data is then processed to generate a 3D digital model representing the scanned object.
Physical Objects
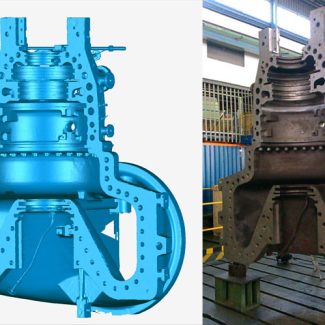
One of the primary applications of 3D scanning in reverse engineering is capturing physical objects. Scanners can accurately capture an object’s intricate details and complex geometry, including its surface texture and color. This process is beneficial when dealing with legacy parts. The original design documentation may need to be made available or completed. Scanning the physical object, engineers can create a digital representation. They can use it as a reference for further analysis and modification.
Digital Models
Once you scan the physical object, the collected data is processed to create a digital model. The point cloud data is converted into a polygon mesh of interconnected triangles. It represents the object’s surface. You can refine this mesh to produce a high-resolution digital model replicating the scanned object. The digital model can be exported in file formats compatible with Computer-Aided Design software. It makes it easier to analyze and change the design.
Analysis and Optimization
With the digital model, engineers can perform various analyses and optimizations. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) can be conducted to check the structural integrity and performance of the part under different loads and conditions. This analysis helps identify potential weak points or areas that need improvement. Engineers can optimize the design by modifying the digital model. They refine its shape, dimensions, or features and simulate the effects of these changes. This iterative process allows for the development of enhanced products or components.
Prototyping and Manufacturing
Reverse engineering is the ability to create prototypes and manufacture replicated parts. Once the digital model is refined and optimized, it can generate 3D printable files. These files are used to fabricate physical prototypes. They use additive manufacturing technologies such as 3D printing. This prototyping process enables engineers to test the functionality of the replicated part. The digital model can also generate tool paths for CNC machining. It allows for the precise production of the replicated part.
3D scanning has revolutionized the field of reverse engineering. It enables engineers to capture physical objects. They create accurate digital models for analysis and reproduction. Engineers can enhance their reverse engineering processes by leveraging the power of 3D scanning. This can lead to improved designs, optimized performance, and more efficient manufacturing.