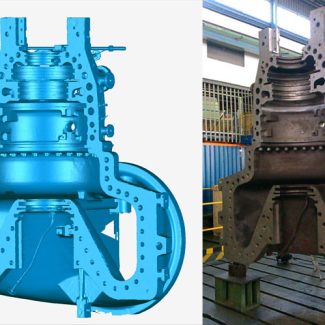
3D scanners use various techniques to collect data points from a real-world object. Types of scanners include laser scanners, structured light scanners, and photogrammetry scanners. Each one has its own way of scanning and unique benefits. Here, we look at how 3D scanning saves time in reverse engineering:
What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a product to better understand its design, construction, and functionality by working backwards from its final form. Reverse engineering is often used to improve upon an existing product or replicate it. Understanding how something works requires access to its design and functionality, especially when blueprints for it no longer exist. This is the case when it comes to older equipment and systems. The original parts may no longer be available.
Reverse engineering requires disassembling a device, such as a computer, to understand what components when into making it and how they all work together. More benefits of reverse engineering include:
– Being able to generate a CAD model for future reference
– Inspiring new ideas from old ideas
– Revamping an obsolete product
– Conducting competitor assessments
There are a few benefits to reverse engineering, but the biggest drawback to consider is how time-consuming and complex the process can be. In addition, the outcome may not be what was expected. Reverse engineering requires commitment as it involves not only time but having to deal with intricate components and systems. Trial and error are frequently part of the reverse engineering process. This can lead to errors in reconstruction. So, what’s that solution?
3D Scanning Benefits Reverse Engineering
3D scanning is the best option for reverse engineering. Compared to conventional techniques, reverse engineering can be a quicker process with 3D scanning. A 3D scanner is more accurate when collecting data. Traditional engineering methods that use calipers and coordinate measuring machines are time-consuming and prone to human error during both the manual measurements and data entry.
3D scanners can capture millions of data points in just seconds. The 3D scan can provide an accurate representation of an object’s makeup. The human error aspect is also solved by using 3D scanning.
When it comes to engineering, time and money matter. By using 3D scanning, you can quickly and more easily prototype, test, and gain feedback on product design. In the event you are working with parts that are no longer produced, redesigning them is easy and accurate.
Gain a Competitive Edge
At Celero, we aim to offer the latest technologies to help you create and improve products that will thrive in the market. We have the expertise to accelerate your design or re-engineering project, whether it’s a cast iron pattern or mold, a machine part, or a facility.
By implementing the use of 3D scanning, reverse engineering becomes less time-consuming and more profitable. At Celero Partners, we offer reverse engineering through the latest 3D scanning hardware and software.